Cyclodextrin mediated cholesterol extraction
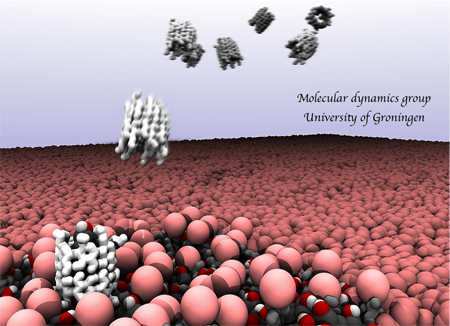
Beta-cyclodextrins (b-CDs) are small cyclic oligosaccharides that can form inclusion complexes with cholesterol, and are commonly used to manipulate cholesterol levels of biomembranes. Although the depletion of cholesterol from membranes, mediated by b-CD is well documented, the molecular details of this process are largely unknown
The MD group uses multiscale molecular dynamics simulations to unravel the mechanism by which CDs, and other inclusion forming agents, act. For instance, we have been able to study the spontaneous, CD mediated, extraction of cholesterol from model membranes, and have calculated the underlying energetics of the process. We expect our research in this area will contribute to the design of more effective cyclodextrin derivatives for medical treatment of lipid metabolism pathologies, like for example in the treatment of Niemann-Pick type C disease.
[1] C.A. Lopez, A.H. de Vries, S.J. Marrink. Computational microscopy of cyclodextrin mediated cholesterol extraction from lipid model membranes Sci. Rep., 3:2071, 2013.
[2] C.A. Lopez, A.H. de Vries, S.J. Marrink. Amylose folding under the influence of lipids. Carbohydr. Res., 364:1–7, 2012.
[3] C.A. López, A.H. de Vries, S.J. Marrink. Molecular Mechanism of Cyclodextrin Mediated Cholesterol Extraction. PLOS Comp. Biol., 7:e1002020, 2011.
| Last modified: | 25 June 2015 01.15 a.m. |
