Goniometric function
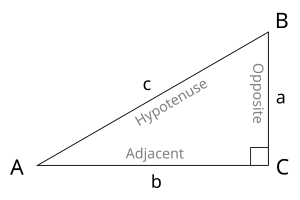
The goniometric functions sinus (sin), cosinus (cos), tangent (tan), cotangent (cot), secant (sec), and cosecant (cst) relate an angle of a right-angled triangle to ratios of two side lengths.
The most common convention is to name the inverse functions using the prefix "arc".
| sin(α) = BC / AB | α = arcsin(BC / AB) | |
| cos(α) = AC / AB | α = arccos(AC / AB) | |
| tan(α) = BC / AC | α = arctan(BC / AC) | |
| cot(α) = AC / BC | α = arccot(AC / BC) | |
| sec(α) = AB / AC | α = arcsec(AB / AC) | |
| csc(α) = AB / BC | α = arccsc(AB / BC) |
| sin(α) = cos(90° - α) | tan(α) = cot-1(α) | |
| sin(α) = -sin(180° - α) | tan(α) = cot(90° - α) | |
| sin(α)2 + cos(α)2 = 1 | tan(α) = -tan(180° - α) | |
| tan(α)2 + 1 = cos(α)-2 | ||
| cot(α)2 + 1 = sin(α)-2 |
Last modified:27 December 2025 10.12 a.m.
View this page in: Nederlands
