Metallic and graphene (nano)foams
Metallic and graphene (nano)foams have excellent properties per unit weight. In addition, they can undergo dimensional changes when a potential difference is applied in an electrochemical environment or when a magnetic field is applied. Here we combine atomistic and continuum techniques to link the porous (nano)structure to their functional and mechanical properties.
1. Highly-porous magneto-active materials for actuation and energy-harvesting
Smart magnetostrictive materials can be used to transform magnetic energy into mechanical energy and vice-versa, making them attractive for actuation and mechanical energy harvesting devices. We use computational techniques to model the magneto-elastic deformation of superparamagnetic and permanently magnetic metal fiber networks and highly-porous polymers containing magnetic nanoparticles.
PhD student: R.P. Singh2. Electrochemical actuation of metallic gyroids
The primary actuation mechanism in the electrochemical actuation of nanofoams is the electric-double layer charging of the internal surface. To account for the excess charge we have developed an atomistic model that is informed by ab-initio density functional theory calculations. We studied the charge-induced actuation strain and work-density of ordered and disordered nanoporous gold and graphene architectures and their differences were critically addressed.
PhD students: S.S.R Saane, E. Detsi. In collaboration with J.Th.M. de Hosson.
Publications (selection)
- Saane, S. S. R., Mangipudi, K. R., Loos, K. U., De Hosson, J. T. M., & Onck, P. R. (2014). Multiscale modeling of charge-induced deformation of nanoporous gold structures. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 66, 1-15. DOI: 10.1016/j.jmps.2014.01.007
- Zinchenko, O., De Raedt, H. A., Detsi, E., Onck, P. R., & De Hosson, J. T. M. (2013). Nanoporous gold formation by dealloying: A Metropolis Monte Carlo study. Computer Physics Communications, 184(6), 1562-1569. DOI: 10.1016/j.cpc.2013.02.004
- Detsi, E., Onck, P., & De Hosson, J. T. M. (2013). Metallic Muscles at Work: High Rate Actuation in Nanoporous Gold/Polyaniline Composites. ACS Nano, 7(5), 4299-4306. DOI: 10.1021/nn400803x
- Detsi, E., Selles, M. S., Onck, P. R., & De Hosson, J. T. M. (2013). Nanoporous silver as electrochemical actuator. Scripta Materialia, 69(2), 195-198. DOI: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2013.04.003
- Saane, S. S. R., De Hosson, J. T. M., & Onck, P. R. (2013). Atomistic modelling of charge-induced deformation of gold nanowires. Modelling and Simulation in Materials Science and Engineering, 21(5), 055024-1-055024-13. [055024]. DOI: 10.1088/0965-0393/21/5/055024
- Detsi, E., Onck, P. R., & De Hosson, J. T. M. (2013). Electrochromic artificial muscles based on nanoporous metal-polymer composites. Applied Physics Letters, 103(19), 193101-1-193101-3. [193101]. DOI: 10.1063/1.4827089
- Detsi, E., Punzhin, S., Rao, J., Onck, P. R., & De Hosson, J. T. M. (2012). Enhanced Strain in Functional Nanoporous Gold with a Dual Microscopic Length Scale Structure. ACS Nano, 6(5), 3734-3744. DOI: 10.1021/nn300179n
- Detsi, E., van de Schootbrugge, M., Punzhin, S., Onck, P. R., & De Hosson, J. T. M. (2011). On tuning the morphology of nanoporous gold. Scripta Materialia, 64(4), 319-322. DOI: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2010.10.023
- Vukovic, I., Punzhin, S., Vukovic, Z., Onck, P., De Hosson, J. T. M., ten Brinke, G., & Loos, K. (2011). Supramolecular Route to Well-Ordered Metal Nanofoams. ACS Nano, 5(8), 6339-6348. DOI: 10.1021/nn201421y
- Detsi, E., Chen, Z. G., Vellinga, W. P., Onck, P. R., & De Hosson, J. T. M. (2011). Reversible strain by physisorption in nanoporous gold. Applied Physics Letters, 99(8), 083104-1-083104-3. [083104]. DOI: 10.1063/1.3625926
- Detsi, E., De Jong, E., Zinchenko, A., Vukovic, Z., Vukovic, I., Punzhin, S., ... De Hosson, J. T. M. (2011). On the specific surface area of nanoporous materials. Acta Materialia, 59(20), 7488-7497. DOI: 10.1016/j.actamat.2011.08.025
3. The micromechanics of metal foams
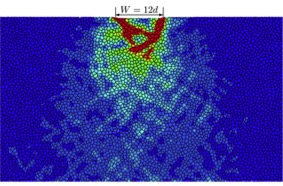
Metal foams have good mechanical properties per unit of mass. In this work we explored the dependence of the stiffness, plastic strength and fracture properties of the foam on the relative density, cellular architecture, specimen size and the properties of the solid metal. We developed finite element methods that account for plastic yielding, hardening and damage development. Along the duration of this work the modelling efforts have been supplemented by experiments carried out in the groups of Lorna Gibson (MIT, USA), Jeff De Hosson (UG) and Katja Loos (UG).
PhD students: C. Tekoglu, K.R. Mangipudi, E. Amsterdam
Publications (selection)
- Mangipudi, K. R., & Onck, P. R. (2012). Tensile failure of two-dimensional quasi-brittle foams. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 49(19-20), 2823-2829. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2012.03.002
- Tekoglu, C., Gibson, L. J., Pardoen, T., & Onck, P. R. (2011). Size effects in foams: Experiments and modeling. Progress in Materials Science, 56(2), 109-138. DOI: 10.1016/j.pmatsci.2010.06.001
- Mangipudi, K. R., & Onck, P. R. (2011). Multiscale modelling of damage and failure in two-dimensional metallic foams. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 59(7), 1437-1461. DOI: 10.1016/j.jmps.2011.02.008
- Mangipudi, K. R., & Onck, P. R. (2011). Notch sensitivity of ductile metallic foams: A computational study. Acta Materialia, 59(19), 7356-7367. DOI: 10.1016/j.actamat.2011.07.071
- Mangipudi, K. R., van Buuren, S. W., & Onck, P. R. (2010). The microstructural origin of strain hardening in two-dimensional open-cell metal foams. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 47(16), 2081-2096. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2010.04.009
- Amsterdam, E., de Vries, J. H. B., De Hosson, J. T. M., & Onck, P. R. (2008). The influence of strain-induced damage on the mechanical response of open-cell aluminum foam. Acta Materialia, 56(3), 609-618. DOI: 10.1016/j.actamat.2007.10.034
- Amsterdam, E., De Hosson, J. T. M., & Onck, P. R. (2008). On the plastic collapse stress of open-cell aluminum foam. Scripta Materialia, 59(6), 653-656. DOI: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2008.05.025
- Amsterdam, E., van Hoorn, H., De Hosson, J. T. M., & Onck, P. R. (2008). The Influence of Cell Shape Anisotropy on the Tensile Behavior of Open Cell Aluminum Foam. Advanced Engineering Materials, 10(9), 877-881. DOI: 10.1002/adem.200800128
- Tekoglu, C., & Onck, P. R. (2008). Size effects in two-dimensional Voronoi foams: A comparison between generalized continua and discrete models. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 56(12), 3541-3564. DOI: 10.1016/j.jmps.2008.06.007
- Amsterdam, E., De Hosson, J. T. M., & Onck, P. R. (2006). Failure mechanisms of closed-cell aluminum foam under monotonic and cyclic loading. Acta Materialia, 54(17), 4465-4472. DOI: 10.1016/j.actamat.2006.05.033
- Tekoglu, C., & Onck, P. R. (2005). Size effects in the mechanical behavior of cellular materials. Journal of Materials Science, 40(22), 5911-5917. DOI: 10.1007/s10853-005-5042-5
- Antoniou, A., Onck, P. R., & Bastawros, A. F. (2004). Experimental analysis of compressive notch strengthening in closed-cell aluminum alloy foam. Acta Materialia, 52(8), 2377-2386. DOI: 10.1016/j.actamat.2004.01.028
- Onck, P. R. (2003). Scale Effects in Cellular Metals. MRS Bulletin, 28(4), 279-283.
- Onck, P. R. (2002). Cosserat modeling of cellular solids. Comptes Rendus. Mécanique, 330(11), 717-722. DOI: 10.1016/S1631-0721(02)01529-2
- Fatemi, J., Keulen, F. V., & Onck, P. R. (2002). Generalized continuum theories: Application to stress analysis in bone. Meccanica, 37(4-5), 385-396. DOI: 10.1023/A:1020839805384
- Andrews, E. W., Gioux, G., Onck, P., & Gibson, L. J. (2001). Size effects in ductile cellular solids. Part II: experimental results. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 43(3), 701-713. DOI: 10.1016/S0020-7403(00)00043-6
- Onck, P. R., Andrews, E. W., & Gibson, L. J. (2001). Size effects in ductile cellular solids. Part I: modeling. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 43(3), 681-699. DOI: 10.1016/S0020-7403(00)00042-4
