
New key publication:Intestinal Farnesoid X Receptor Controls Transintestinal Cholesterol Excretion in Mice.
Intestinal Farnesoid X Receptor Controls Transintestinal Cholesterol Excretion in Mice
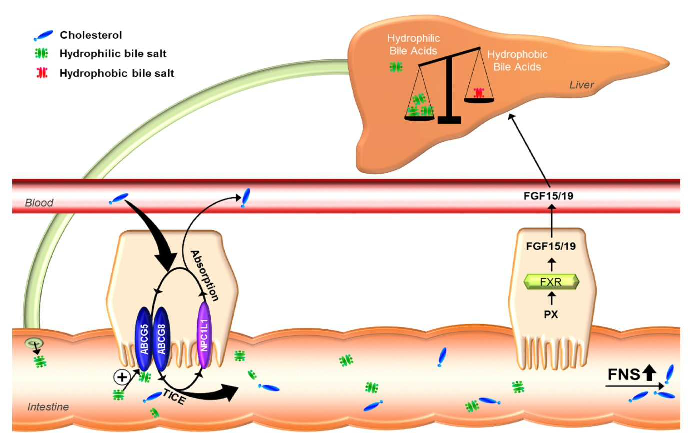
PX20606 (PX) activates FXR in the intestine, leading to the production of FGF15/19 which, in turn, causes a shift in bile salt pool composition towards more hydrophilic bile salts. At the level of the enterocyte, excretion of cholesterol from the cell into the intestinal lumen is induced in a manner that largely depends on the activity of ABCG5/G8. As the amount of ABCG5/G8 protein on the brush border membrane remains unchanged upon PX treatment, the transport activity must be increased. Hydrophilic bile salts may facilitate increased export of cholesterol from enterocytes by ABCG5/G8. When re-uptake of exported cholesterol is blocked by addition of ezetimibe to the diet of PX-treated mice, this leads to even further increased cholesterol disposal from the body.
More:
More news
-
15 September 2025
Successful visit to the UG by Rector of Institut Teknologi Bandung
