
New Key Publication: A Human-like Bile Acid Pool Induced by Deletion of Hepatic Cyp2c70 Modulates Effects of FXR Activation in Mice, included:Commentary 2020
Abstract
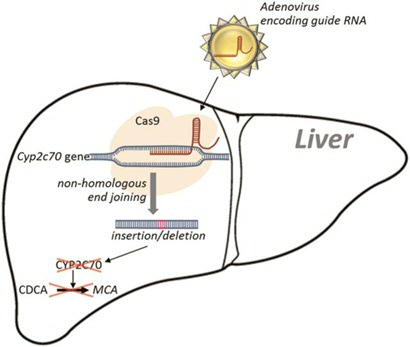
Bile acids (BAs) facilitate intestinal absorption of lipid-soluble nutrients and modulate various metabolic pathways through the farnesoid X receptor (FXR) and Takeda G-protein-receptor 5. These receptors are targets for therapy in cholestatic and metabolic diseases. However, dissimilarities in BA metabolism between humans and mice complicate translation of preclinical data. CYP2C70 was recently proposed to catalyze the formation of rodent-specific muricholic acids (MCAs). With CRISPR/Cas9-mediated somatic genome editing, we generated an acute hepatic Cyp2c70 knock-out mouse model (Cyp2c70 ako ) to clarify the role of CYP2C70 in BA metabolism in vivo and evaluate whether its activity modulates effects of pharmacologic FXR activation on cholesterol homeostasis. In Cyp2c70 ako mice, chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA) increased at the expense of BMCA, resulting in a more hydrophobic, human-like BA pool. Tracer studies demonstrated that, in vivo, CYP2C70 catalyzes the formation of BMCA primarily by sequential 6B- hydroxylation and C7-epimerization of CDCA, generating AMCA as an intermediate metabolite. Physiologically, the humanized BA composition in Cyp2c70 ako mice blunted the stimulation of fecal cholesterol disposal in response to FXR activation compared with wild-type mice, predominantly due to reduced stimulation of transintestinal cholesterol excretion. Thus, deletion of hepatic Cyp2c70 in adult mice translates into a human-like BA pool composition and impacts the response to pharmacologic FXR activation. This Cyp2c70 ako mouse model may be a useful tool for future studies of BA signaling and metabolism that informs human disease development and treatment.
- Jan Freark de Boer
- Esther Verkade
- Niels L. Mulder
- Hilde D. de Vries
- Nicolette Huijkman
- Martijn Koehorst
- Theo Boer
- Justina C. Wolters
- Vincent W. Bloks
- Bart van de Sluis
- Folkert Kuipers
JLR: http://www.jlr.org/content/early/2019/09/10/jlr.RA119000243
Commentary: ( 21/1/2020) : Is CYP2C70 the key to new mouse models to understand bile acids in humans?
JLR: http://www.jlr.org/content/early/2020/01/21/jlr.C120000621.abstract
More news
-
15 September 2025
Successful visit to the UG by Rector of Institut Teknologi Bandung
