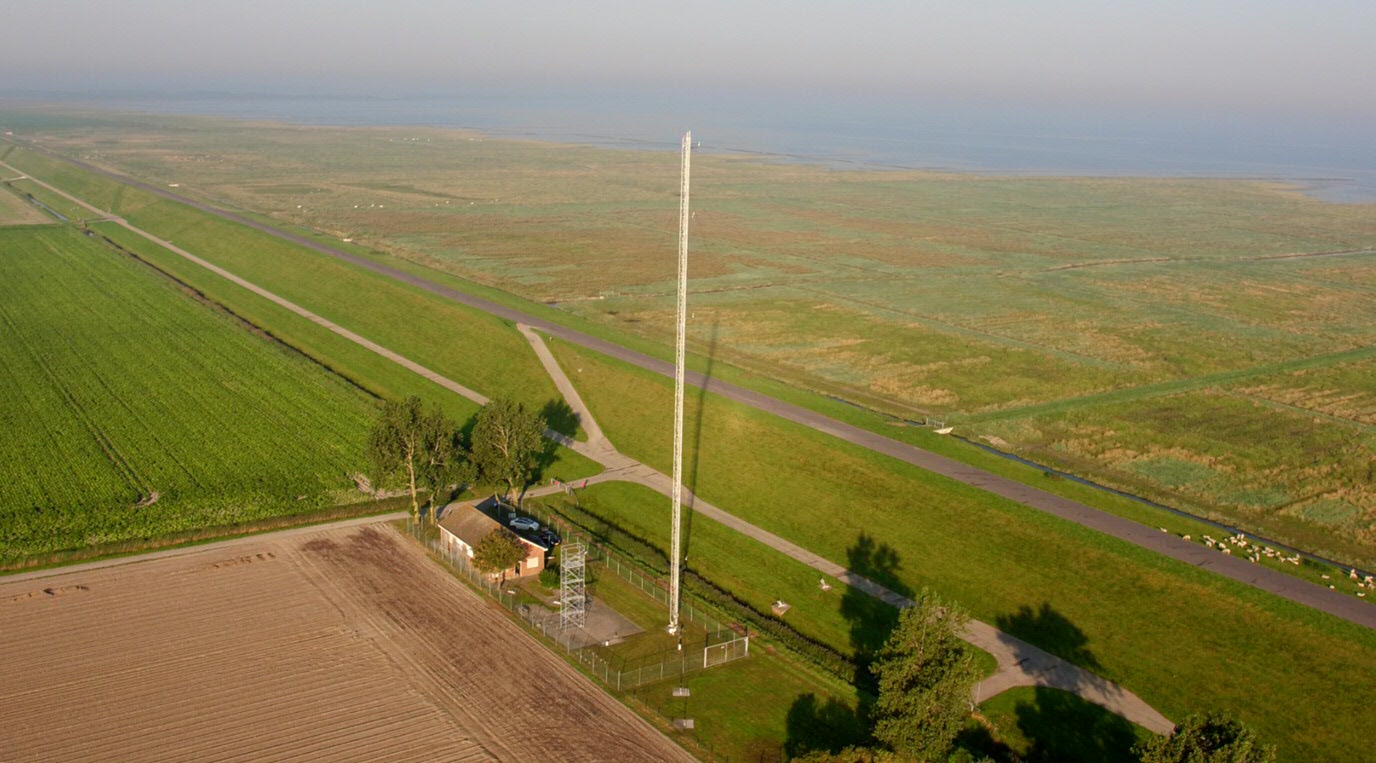
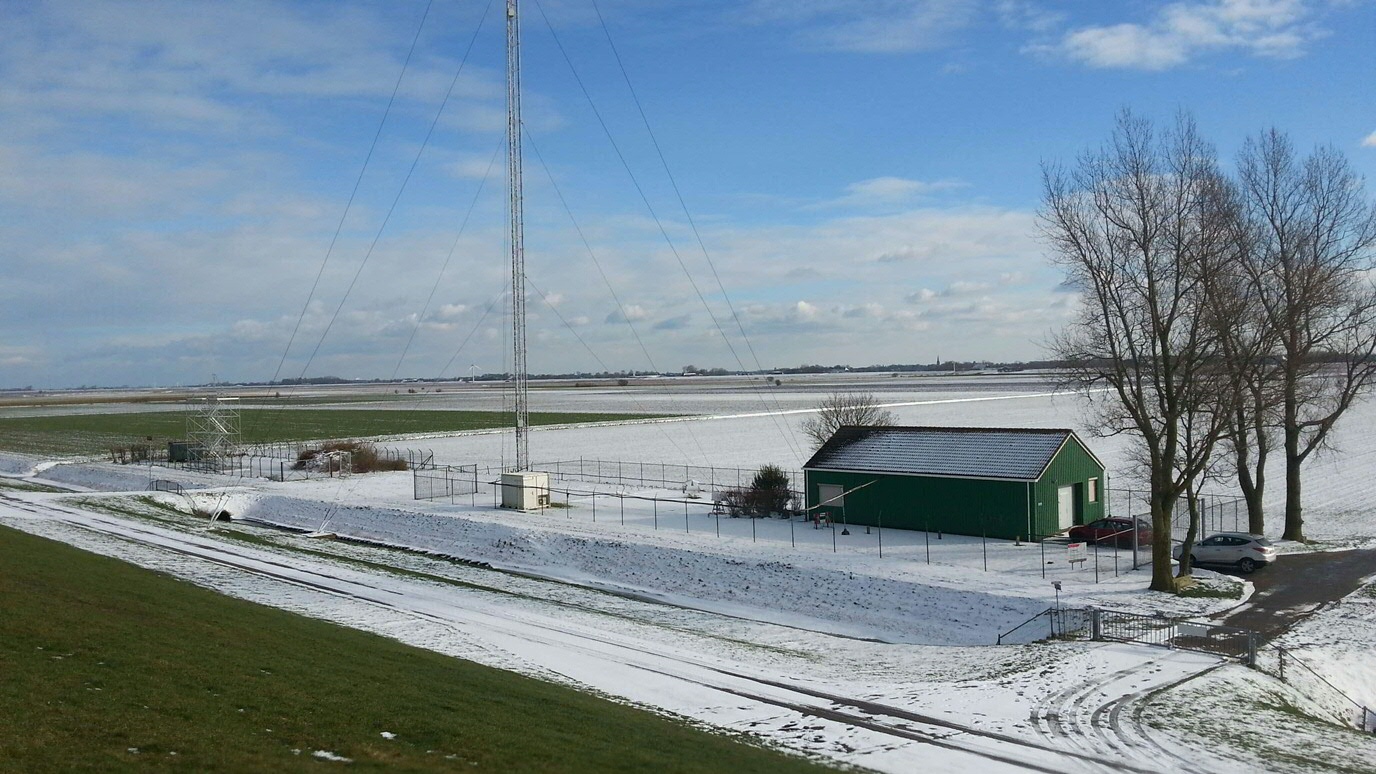
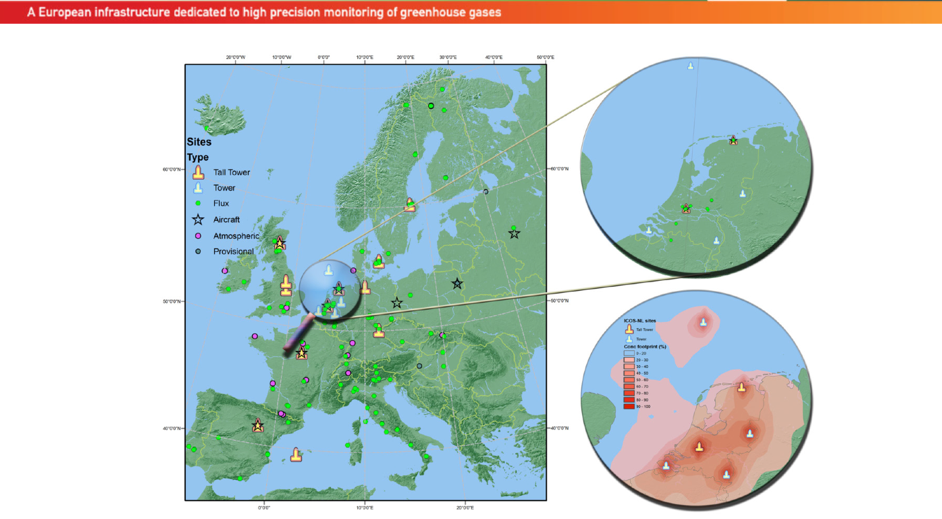
Lutjewad measurement station
The Center for Isotope Research of the University of Groningen has had an atmospheric measurement station on the Wadden Sea dike near Hornhuizen since 2000.
The measuring station consists of a high mast of 60 meters with next to it a small building containing a laboratory. The laboratory was completely renovated in the autumn of 2013. The mast contains measuring equipment for research into the greenhouse effect and there are air inlets at heights of 7, 40 and 60 meters. Air is pumped to the lab through these inlets. All kinds of measurements are taken on the spot. Glass bottles are also automatically filled and taken to Groningen for analysis. The container and the scaffolding mast were placed and put into use in 2020 and 2021.

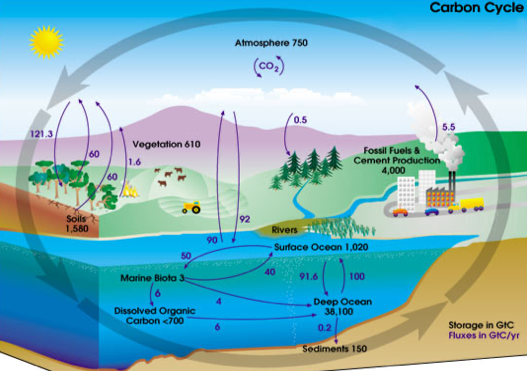
The main gas measured in Lutjewad is the greenhouse gas carbon dioxide (CO2). This gas already occurs naturally in the air, but the large-scale combustion of fossil fuels (natural gas, coal, oil) is releasing more and more CO2 into the atmosphere. By measuring the isotopes 13CO2 and 14CO2 and all kinds of so-called tracers in addition to the CO2 concentration, more information can be obtained about the origin of the measured CO2. In addition, we also measure the lesser-known greenhouse gases methane (CH4) and nitrous oxide (N2O).
Measurement data from Lutjewad station is linked to measurement data from similar stations elsewhere in the world in order to get an increasingly better picture of the changing atmosphere.
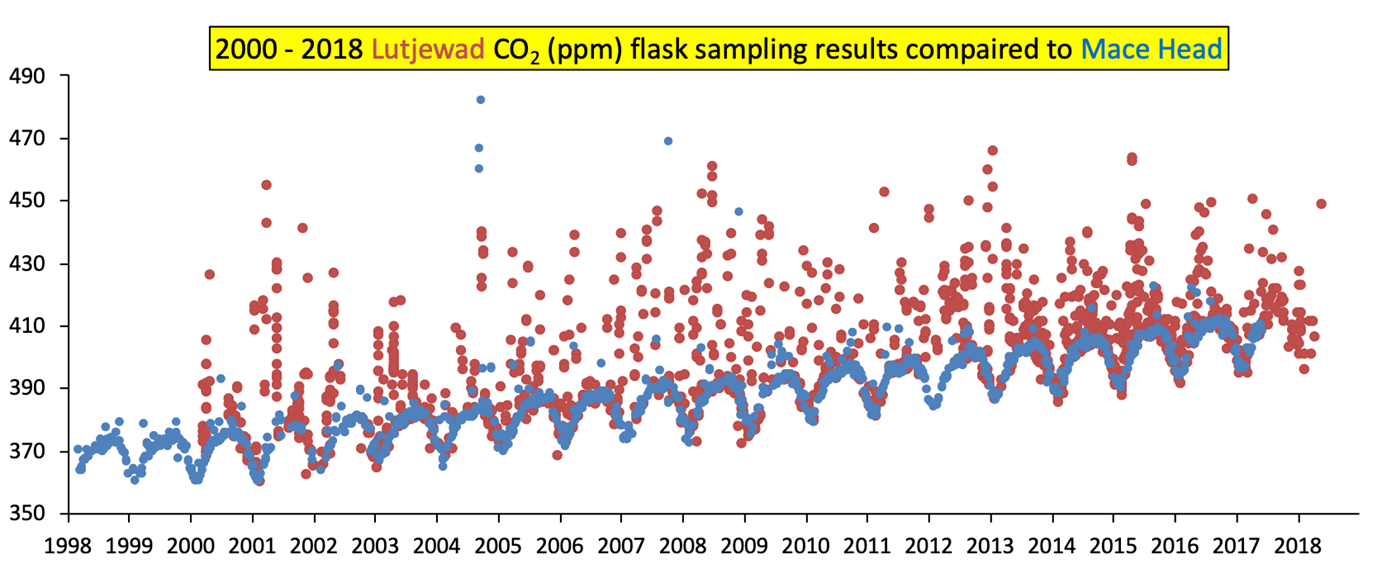
The location at Hornhuizen is ideal for atmospheric measurements as it is far from major disruptive carbon dioxide sources such as factories. The height of the mast ensures that local resources, such as the farmer's tractor, are not measured either. In this way, really clean European background air is measured in a northerly wind. South winds measure air that is regionally influenced by both the biosphere and humans.
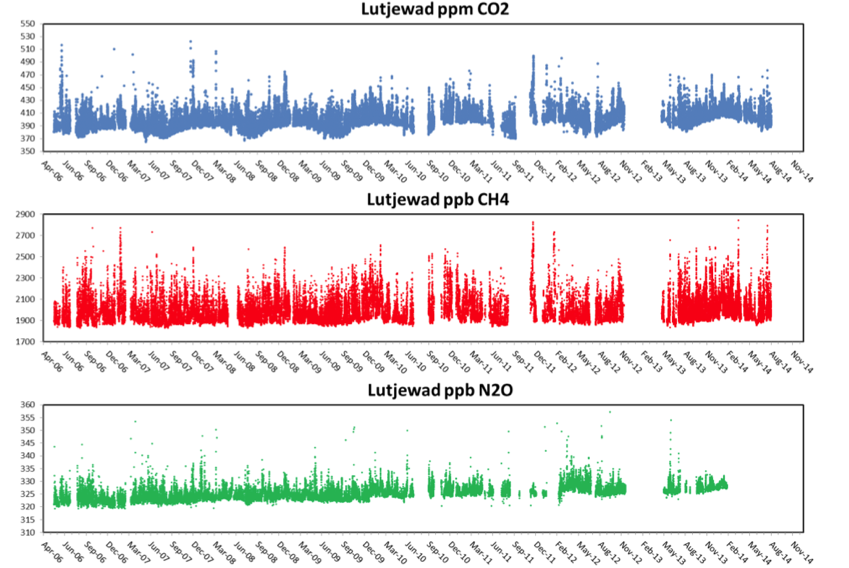
All kinds of particulate matter (aerosol) measurements are also taken and samples are taken in the small container and the scaffolding mast, from a height of 20 m. Particulate matter is an important component of air pollution due to the use of fossil fuels (and biomass). In addition to health effects, particulate matter also plays an important role in the Earth's climate because it influences cloud formation and thus precipitation and because, depending on its composition, it has a cooling or warming effect in the atmosphere. Research into particulate matter on Lutjewad focuses in particular on the sources, source strength and chemical composition of particulate matter.
There are two 'drop radar systems' on the scaffolding mast, in collaboration with Delft University of Technology. These measure the droplet size in the atmosphere, up to about 10 km away. This is again linked to the amount of particulate matter in the air.
Real time data
GHG monitoring
Timeseries:
- 3 days | for Lutjewad go to P0004.4_LUT_465.png
- 10 days | for Lutjewad go to P0004.3_LUT_465.png
- last month | for Lutjewad go to P0004.3_2_LUT_465.png
- last year | for Lutjewad go to P0004.3_1_LUT_465.png
Meteorological measurements
Timeseries:
- 3 days | for Lutjewad go to P0005.04_LUT.png
- 10 days | for Lutjewad go to P0005.03_LUT.png
- last month | for Lutjewad go to P0005.02_LUT.png
- last year | for Lutjewad go to P0005.01_LUT.png
Visit related websites
- The European Network (ICOS) | https://icos-atc.lsce.ipsl.fr
- Ruisdeal observatory. Atmospheric research groups in the Netherlands| https://www.ruisdael-observatory.nl
- Was het donker? Een donker sensor op locatie Hornhuizen (Lutjewad) | http://www.washetdonker.nl
- TU Delft. Remote sensing usiing radar systems | https://www.tudelft.nl/citg/over-faculteit/afdelingen/geoscience-remote-sensing
- KNMI | https://www.knmi.nl/kennis-en-datacentrum/uitleg/meetmast-cabauw
- Lightning detection network. Lutjewad will be one of the measuring points | https://www.knmi.nl/kennis-en-datacentrum/uitleg/bliksemmetingen
- RIVM has a fine dust sensor netwo throughout the Netherlands. Lutjewad is one of the stations | https://samenmeten.rivm.nl/dataportaal/
| Last modified: | 17 January 2022 3.21 p.m. |