Schilderijen wijzen de weg naar chips die werken op licht

Wetenschappers van het Zernike Instituut voor Geavanceerde Materialen van de RUG hebben twee beroemde schilderijen nagemaakt op een schaal van duizendste millimeters. Dat was niet alleen een eerbetoon aan Johannes Vermeer en Vincent van Gogh, maar vooral een bewijs dat het mogelijk is piepkleine optische systemen te maken.
FSE Science Newsroom | René Fransen
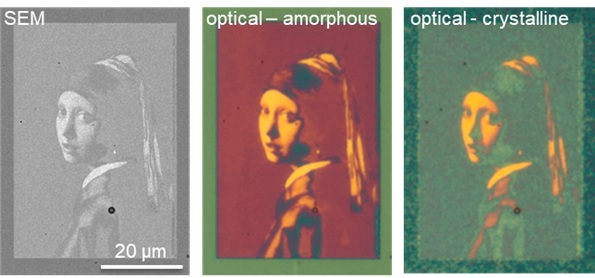
Het canvas voor deze reproducties bestaat uit een laag van reflecterend goud. Daarop brachten de wetenschappers een dunne film van antimoon/selenium (Sb2Se3) aan. Dit gebeurde onder leiding van professor Bart Kooi, die materialen maakt met een structuur op de schaal van nanometers (miljoenste millimeters). Licht dat terugkaatst van het goud, en daarbij door de dunne film gaat, kan verschillende kleuren aannemen, afhankelijk van de dikte van de film. Dit is hetzelfde fenomeen dat je kunt zien wanneer er een laagje olie op water ligt, ook dan zie je allerlei kleuren.
Lithografie
De afbeeldingen zijn eerst overgezet in pixels met grijstinten. Vervolgens is een krachtige straal geladen deeltjes gebruikt om stukjes van de film weg te frezen, op een diepte die correspondeert met de grijswaarde van de pixels, die een afmeting van enkele nanometers hebben. Licht dat via de dunne film terugkaatst krijgt een kleur die afhankelijk is van de dikte van de film, en het resultaat laat het ‘Meisje met de parel’ van Vermeer in kleur zien (zie afbeelding). Hetzelfde is gedaan met de Sterrenhemel van Van Gogh.
Deze verkleinde kunstwerken laten zien dat het mogelijk is om met een straal geladen deeltjes op een schaal van nanometers pixels te maken, waarbij het hoogteverschil niet in stapjes verloopt maar continu is. Dit soort pixels zijn niet te maken met gewone technieken, zoals lithografie. En omdat het antimoon/selenium een zogeheten fase-veranderend materiaal is, is het ook mogelijk de eigenschappen van de pixels te veranderen door hun structuur met elektrische pulsen aan te passen.
Deze kleine pixels zijn mogelijk te gebruiken in beeldschermen, maar een meer voor de hand liggende optie is het maken van optische chips (schakelingen die werken op licht in plaats van elektrische stroom) en andere optisch-elektronische toepassingen.
Het onderzoek is op 1 september gepubliceerd in het tijdschrift Advanced Materials .
Meer nieuws
-
10 maart 2026
Microplastics als een boemerang
-
17 februari 2026
De lange zoektocht naar nieuwe fysica
-
10 februari 2026
Waarom slechts een klein aantal planeten geschikt is voor leven
