De Melkweg deint
Een internationaal team van astronomen, onder wie Amina Helmi van de Rijksuniversiteit Groningen, heeft ontdekt dat de Melkweg een golfbeweging maakt. Het team heeft voor deze ontdekking gebruik gemaakt van het RAdial Velocity Experiment (RAVE) dat een half miljoen sterren rond de zon in kaart heeft gebracht. Uit het onderzoek blijkt dat de Melkweg - buiten de bekende rotatie rond het galactisch centrum - loodrecht op het galactisch vlak beweegt. Het onderzoek is gepubliceerd in het tijdschrift Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
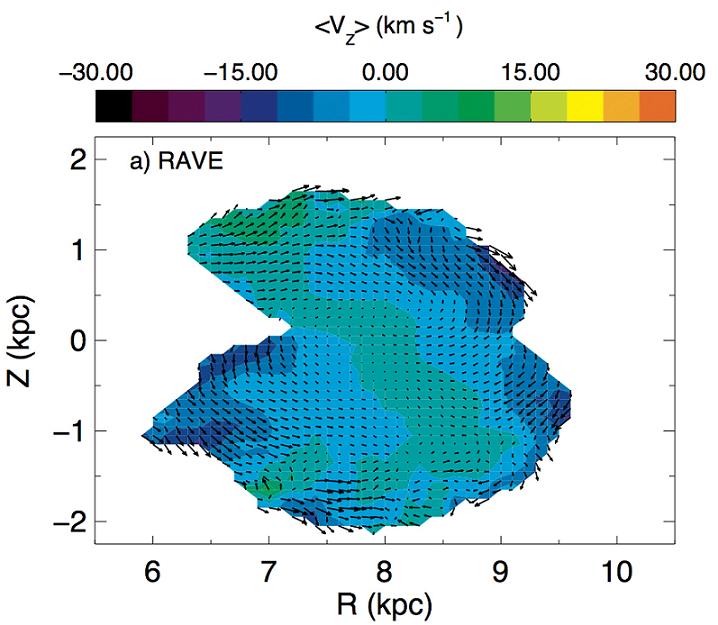
De astronomen brachten de snelheden in kaart van sterren in een driedimensionale regio rond de zon, die een gebied beslaat met een straal van 6500 lichtjaar, en tot een kwart van de afstand tot het Melkwegcentrum reikt. Het team gebruikte een klasse van rode reuzensterren (zogeheten 'red clumpsterren'), die bijna allemaal even helder zijn, waardoor het het mogelijk is om de afstand tot deze sterren vast te stellen. De snelheden die zijn bepaald met RAVE werden gecombineerd met gegevens van andere surveys, waardoor met een ongekend groot aantal red clumpsterren driedimensionale snelheden in een groot gebied rond de zon konden worden bestudeerd.
Uit de analyse blijkt dat de Melkweg niet alleen rond zijn centrum draait, maar ook kleine golvende of zuigende bewegingen maakt. Ons sterrenstelsel gedraagt zich als een enorme vlag die wappert langs het galactisch vlak. Het chaotische golfpatroon ontstaat door krachten uit verschillende richtingen. De bron van de krachten is nog niet bekend. Mogelijk veroorzaken de spiraalarmen de golfbewegingen, maar een andere verklaring zou kunnen zijn dat een klein melkwegstelsel door het onze beweegt.
De driedimensionale bewegingspatronen vertonen ingewikkelde structuren. De opwaartse en neerwaartse snelheden laten een golfachtige beweging zien, met sterren die naar binnen en naar buiten worden geslingerd. “Vroeger dachten we dat de Melkweg een stabiel en tijdonafhankelijk systeem was, maar nu zien we dat er processen gaande zijn die we nog niet zo goed begrijpen, en die leiden tot deze complexe patronen die we niet hadden verwacht”, zegt Helmi. "We willen de driedimensionale modellen van de Melkweg nu verder verfijnen om de snelheidsverdeling van sterren in de Melkweg werkelijk te kunnen doorgronden."
The wobbly Galaxy: kinematics north and south with RAVE red-clump giants, M. E. K. Williams et al., MNRAS (2013), DOI: 10.1093/mnras/stt1522