Research Highlight
Prof. dr. Ida van der Klei
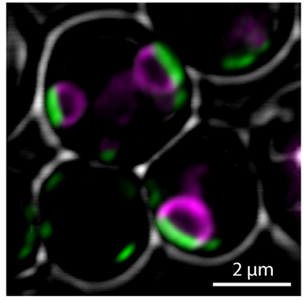
Peroxisomes are crucial cell organelles. Common functions include lipid and hydrogen peroxide metabolism, but peroxisomes also can fulfil many other metabolic and non-metabolic roles. Recently, we identified and characterized several peroxisomal membrane contact sites. Membrane contact sites are defined as regions of close proximity between two membranes, associated by protein-protein and/or protein-lipid interactions. Using electron microscopy, we showed that yeast peroxisomes form contacts with most other cell organelles (e.g. the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), mitochondria, vacuoles) and with the plasmamembrane[1]. We identified several contact site resident proteins that are required for the formation and/or function of peroxisomal contact sites[1-4]. The peroxisomal membrane protein Pex3 plays a role in peroxisome-plasmamembrane and peroxisome-vacuole contacts. Inp1 (inheritance of peroxisomes 1), a protein required for peroxisome retention in yeast mother cells, is recruited to peroxisomes by Pex3. Analysis of truncated Inp1 variants revealed that the C-terminus of Inp1 interacts with Pex3, while the extreme N-terminal domain and a conserved middle homology domain (MHD) are involved in association of Inp1 to the plasmamembrane. The MHD is predicted to fold as a divergent pleckstrin homology (PH)-like domain, which is most likely involved in protein-protein interactions[2]. Pex3 is essential for the formation of peroxisome vacuole contacts[1]; however, the exact function of this contact is still unknown. Proteins of the Pex23 family are important for the formation of peroxisome-ER contacts[3] and these proteins also localize to the ER. Most likely these peroxisome-ER contact sites play a role in lipid transport from the ER to peroxisomes allowing expansion of the peroxisomal membrane[3,4].
[1] Wu H, de Boer R, Krikken AM, Aksit A, Yuan W & van der Klei IJ (2019). Peroxisome development in yeast is associated with the formation of Pex3-dependent peroxisome-vacuole contact sites. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta Molecular Cell Research 1866, 349-359.
[2] Krikken AM, Wu H, de Boer R, Devos DP, Levine TP & van der Klei IJ (2020). Peroxisome retention involves Inp1-dependent peroxisome-plasma membrane contact sites in yeast. Journal of Cell Biology 219(10): e201906023.
[3] Wu F, de Boer R, Krikken AM, Aksit A, Bordin N, Devos DP & van der Klei IJ (2020). Pex24 and Pex32 are required to tether peroxisomes to the ER for organelle biogenesis, positioning and segregation in yeast. Journal of Cell Science 133(16): jcs246983.
[4] Wu F, de Boer R & van der Klei IJ (2023) Gluing yeast peroxisomes: composition and function of membrane contact sites. Journal of Cell Science 136 (11): 259440.
| Last modified: | 24 October 2023 2.33 p.m. |
