Encryption for research: safeguarding sensitive data
With the ever-present risk of data breaches and unauthorized access, encryption tools play a crucial role in ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of research findings. Our supported solution, VeraCrypt, is a versatile and open-source program designed to protect data across multiple platforms.
In this article, we delve into the fundamentals of encryption, its importance in research, who should consider incorporating it into their workflow, and the reasons why we support VeraCrypt.
Understanding encryption
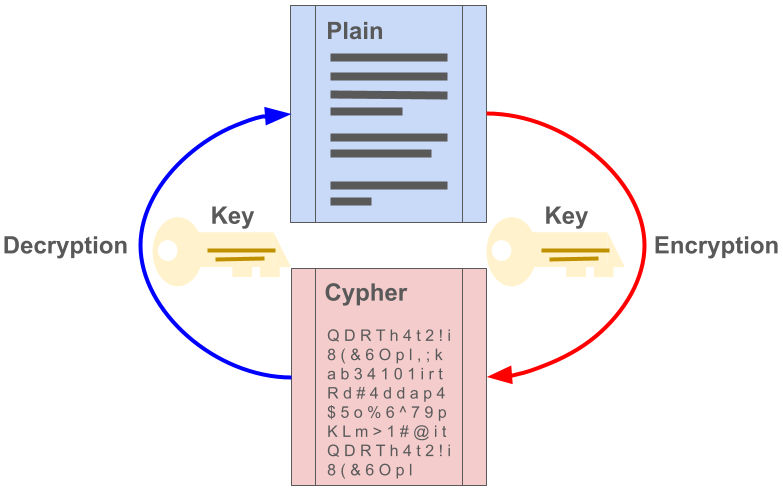
Encryption is the process of transforming plaintext, the original human and machine-readable information contained in a file or piece of media, into ciphertext, a scrambled version of the data that is indecipherable without the appropriate decryption key. This transformation is achieved through (mathematical) formulas or algorithms, ranging from simple to highly complex. A historical example of early encryption is the system used by famous Roman general Caius Julius Caesar. His method was shifting each letter in a message by three places in the Latin alphabet.
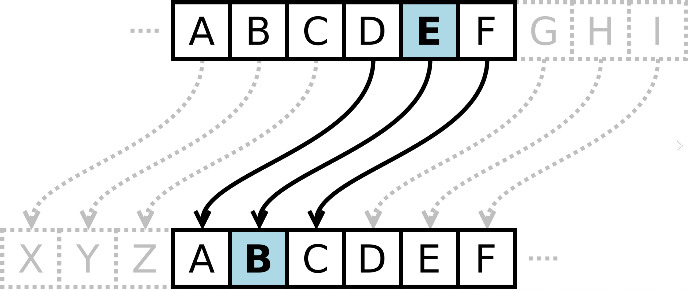
In modern times, data encryption has become much more complex and serves as a robust security method, ensuring that information remains encoded and can only be accessed or decrypted by individuals possessing the correct encryption key. Modern encryption standards such as AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) and tools such as VeraCrypt provide researchers with means to safeguard their data against unauthorized access and malicious threats.
The importance of encryption for research
The purpose of data encryption is to protect the confidentiality of digital data as it is stored on computer systems and transmitted over the Internet or other computer networks. While encryption can be used by anyone for a variety of purposes, its importance is critical for researchers working with sensitive data. Given that we are connected almost all the time, it is important that information that needs to be protected from unwanted attention can be stored securely during and after research.
Encryption can be used in particular to secure data, on a temporary or permanent basis, in situations and environments where there is uncertainty about the overall security measures or their implementation. In cases where researchers work outside of the University premises, it is a good idea to add a layer of protection to the data that is being processed or gathered. Having an encrypted folder on their laptop, or setting up an encrypted folder on a machine they are not the only user of, will help protect their data and findings from potential security threats.
In addition, encryption plays a key role in protecting individuals' personal information and beliefs by ensuring that such data is protected from unauthorized access. This is particularly important when researchers are recording and storing information that requires a high level of confidentiality.
Who should use encryption in research?
Encryption can be used by any researcher, but it is particularly useful for those working with sensitive data. Additionally, researchers who frequently operate outside the UG premises and collect confidential information on their laptops should consider encryption as an essential part of their research toolkit.
Moreover, encryption serves as a proactive measure in adherence to regulatory frameworks and institutional guidelines governing data protection and privacy. By incorporating encryption practices into research protocols, academic institutions and individual researchers affirm their commitment to protecting the rights and confidentiality of research participants.
Introducing VeraCrypt
VeraCrypt is an open source encryption program designed to strengthen data security across different operating systems. Developed as the open source successor to TrueCrypt, VeraCrypt allows users to encrypt and decrypt individual files and folders on the machine on which it is installed, ensuring that sensitive information remains inaccessible to unauthorized parties.

VeraCrypt uses advanced encryption algorithms, primarily but not limited to the highly secure AES, to encode data within encrypted volumes. Once encrypted, a folder appears as random data until decrypted with VeraCrypt, providing an additional layer of security against prying eyes.
An important aspect to note is that decryption and encryption are exclusively handled by VeraCrypt. The program makes sure that all plaintext information decrypted during use is stored solely in RAM, minimizing the risk of data exposure even after the volume is closed and the decryption process has concluded.
VeraCrypt vs. BitLocker
There is no shortage of encryption programs available online. University-provided Windows workstations are set up with access to BitLocker, which is a good option for general use. However, when handling sensitive research data it is important to ensure additional security features are available. Using VeraCrypt as an additional tool provides enhanced security for research data.
BitLocker covers:
-
Windows systems exclusively - except for the Home edition - limiting the compatibility with other operating systems.
-
The encryption of entire system drives. Once the decryption process starts, the entire drive is rendered in plaintext, which can potentially expose sensitive research data.
-
A closed source code, as a downside. It is not possible to check for vulnerabilities and backdoors, if any are present.
Advantages of VeraCrypt:
-
Cross-platform compatibility ensures seamless decryption across different operating systems, including Windows, Linux and MacOS, offering flexibility to researchers working across diverse environments.
-
Encryption and decryption of individual files and folders provide granular control over data security, reducing the risk of unintentional exposure.
-
The creation of keyfiles, a feature not available in BitLocker, allows carrying part of the “password” separately, thus making access to data impossible unless in possession of the keyfile.
-
The ability to choose encryption protocols enhances security and customization options, catering to the specific needs of researchers.
-
As an open-source program users can scrutinize the code for vulnerabilities. An open source code does not mean an open key, the algorithm used does not allow the reverse engineering of the key.
Why do we support VeraCrypt?
At the Digital Competence Centre of the University of Groningen (UG DCC), we support VeraCrypt as an encryption tool for researchers to protect their data. Here's why in a nutshell:
-
Cross-platform compatibility: Whether you're working on a university machine or from the comfort of your home using a Linux device, VeraCrypt ensures seamless decryption without the need for software alterations.
-
Open-source integrity: VeraCrypt's open-source architecture fosters trust and transparency, empowering users to validate its security features and contribute to its ongoing development.
-
Strong encryption standards: With its support for robust encryption algorithms and customizable security options, VeraCrypt offers unparalleled protection for sensitive research data.
-
High-security standards: VeraCrypt meets the high-security standards of our University.
Conclusion
In conclusion, encryption is an indispensable safeguard in the pursuit of ethical and secure research practices. By using encryption methods, researchers not only strengthen the integrity of their scientific work, but also uphold the principles of privacy and confidentiality that are essential to the advancement of knowledge in the digital age. As custodians of sensitive information, researchers have a collective responsibility to use encryption technologies as a cornerstone of ethical research conduct in an increasingly interconnected world.

| Last modified: | 21 March 2024 3.39 p.m. |
More news
-
29 April 2024
Tactile sensors
Every two weeks, UG Makers puts the spotlight on a researcher who has created something tangible, ranging from homemade measuring equipment for academic research to small or larger products that can change our daily lives. That is how UG...
-
16 April 2024
UG signs Barcelona Declaration on Open Research Information
In a significant stride toward advancing responsible research assessment and open science, the University of Groningen has officially signed the Barcelona Declaration on Open Research Information.
-
02 April 2024
Flying on wood dust
Every two weeks, UG Makers puts the spotlight on a researcher who has created something tangible, ranging from homemade measuring equipment for academic research to small or larger products that can change our daily lives. That is how UG...

